how can biomass energy be used
How Biomass Is Powering Communities
Biomass energy is an emerging renewable energy source that is gaining traction worldwide. It involves using organic materials, such as agricultural residues, wood pellets, and even animal waste, to generate heat, electricity, and other forms of power. This article explores the benefits and significance of biomass energy in powering communities.
What is biomass energy?
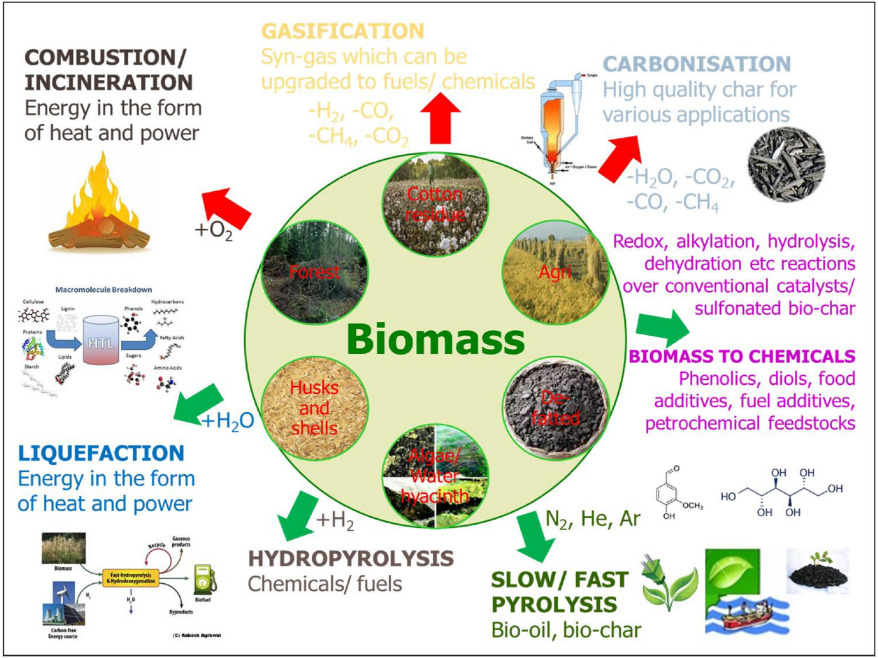
Biomass energy refers to the use of organic materials derived from plants and animals to generate renewable energy. It is derived from various sources, including forestry and agricultural residues, dedicated energy crops, and animal by-products. These organic materials are converted into heat, electricity, or another form of power through different technologies, such as combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion.
Benefits of biomass energy:
- Renewable and sustainable source of energy
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions
- Helps in waste management and recycling
- Creates local jobs and stimulates economic growth
- Contributes to energy independence
Case study:
For example, in a rural community in Asia, the establishment of a biomass power plant has revolutionized their energy landscape. The plant uses agricultural residues, such as rice husks and corn stalks, as feedstock to generate electricity. This has not only provided a reliable source of energy for the community but has also created job opportunities for the locals. Additionally, it has significantly reduced the community's dependence on fossil fuels and lowered their carbon footprint.
How can biomass energy benefit you?

Biomass energy offers several advantages for individuals, communities, and businesses. Here are some ways biomass energy can benefit you:
- 1. Energy cost savings: By utilizing biomass energy, you can reduce your reliance on conventional energy sources, such as fossil fuels, which can be expensive. Biomass energy provides a more affordable alternative.
- 2. Environmental sustainability: Biomass is a renewable energy source that produces significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels. By switching to biomass energy, you can contribute to a greener and more sustainable future.
- 3. Improved waste management: Biomass energy can help tackle the issue of organic waste management. It utilizes agricultural residues, forest wastes, and animal by-products that would otherwise contribute to pollution or pose disposal challenges.
- 4. Job creation: The establishment of biomass power plants and facilities requires a skilled workforce. This creates employment opportunities, contributing to local economic growth and development.
- 5. Energy independence: By diversifying energy sources and reducing dependence on imported fuels, biomass energy enhances energy security and independence for both individual households and entire communities.
Study case:
In a study conducted in a metropolitan area, a housing community transitioned to biomass heating systems for their buildings. This switch not only resulted in cost savings for the residents but also reduced their carbon emissions by a significant margin. The implementation of biomass energy systems also led to the creation of jobs in the region, boosting the local economy.
12 Most Asked Questions about Biomass Energy
1. How does biomass energy work?
Biomass energy can be generated through different conversion technologies. The most common methods include combustion, gasification, and anaerobic digestion. In combustion, organic materials are burned to produce heat, which can be used directly or converted into electricity. Gasification involves converting biomass into a gas fuel, which can then be utilized for various applications. Anaerobic digestion, on the other hand, involves the breakdown of organic matter by bacteria, generating biogas that can be used as a source of energy.
2. What types of biomass can be used for energy production?
Various types of biomass can be used for energy production, including agricultural residues (such as crop stubble and husks), forestry residues (like wood chips and bark), dedicated energy crops (such as switchgrass and miscanthus), municipal solid waste, and even animal manure. These biomass sources can be converted into energy through different processes depending on the characteristics of the feedstock.
3. Is biomass energy renewable?
Yes, biomass energy is considered a renewable energy source. As long as the organic materials used for biomass energy production are derived from sustainable sources and their growth and regeneration are properly managed, biomass energy can be continuously produced without depleting natural resources.
4. What are the environmental benefits of biomass energy?
Biomass energy has several environmental benefits, including:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but the carbon emitted is part of the natural carbon cycle. Additionally, using biomass as an alternative to fossil fuels helps prevent the release of additional carbon dioxide from the extraction and combustion of fossil fuels.
- Promotes sustainable land use: Growing energy crops for biomass can help restore and protect degraded lands, improve soil quality, and enhance biodiversity.
- Reduces dependence on fossil fuels: Utilizing biomass energy reduces reliance on finite fossil fuel resources, helping to mitigate the associated environmental impacts of fossil fuel extraction and combustion.
5. Can biomass energy help reduce waste?
Yes, biomass energy can help reduce waste by utilizing organic materials that would otherwise end up in landfills or contribute to pollution. It offers an efficient means of managing agricultural residues, forest wastes, and organic waste from industries and municipalities.
6. Is biomass energy economically viable?
Biomass energy can be economically viable under the right conditions. Factors such as the availability and cost of biomass feedstock, the efficiency of conversion technologies, government incentives and policies, and the scale of operation all play a role in determining the economic viability of biomass energy projects.
7. What are the challenges associated with biomass energy?
Some challenges associated with biomass energy include:
- Availability and logistics of biomass feedstock: Ensuring a consistent supply of biomass feedstock can be challenging, especially in regions where the availability of organic materials is limited or in high demand for other uses.
- Efficiency of conversion technologies: Different conversion technologies have varying levels of efficiency, and improving efficiency is crucial for maximizing the energy output from biomass feedstock.
- Emissions and air pollution: While biomass combustion generally produces lower emissions compared to fossil fuels, it can still contribute to air pollution if not properly managed.
8. How does biomass energy compare to other renewable energy sources?
Biomass energy offers several advantages over other renewable energy sources:
- Energy storage: Biomass energy can be stored and used when needed, unlike some renewable sources like solar or wind, which rely on weather conditions.
- Continuous power generation: Biomass power plants can provide a stable and consistent power supply, as they are not dependent on intermittent sources like solar or wind.
- Utilization of waste materials: Biomass energy can make productive use of organic waste materials that would otherwise go unused or become a disposal problem.
9. How can individuals contribute to biomass energy adoption?
Individuals can contribute to biomass energy adoption by:
- Using biomass heating systems or stoves for residential spaces
- Supporting local initiatives and campaigns promoting biomass energy
- Advocating for favorable government policies and incentives to encourage biomass energy projects
- Considering biomass energy options when making energy-related decisions, such as choosing renewable energy providers
10. Is biomass energy suitable for all regions?
Biomass energy can be suitable for various regions, but its viability depends on factors such as the availability of biomass feedstock, climate conditions, and government support. Regions with abundant agricultural or forestry resources tend to have greater potential for biomass energy production.
11. How scalable is biomass energy?
Biomass energy can be scaled up or down depending on the energy demand of a particular area. Biomass power plants can be developed in different sizes, from small-scale systems for individual households to large industrial facilities. The scalability of biomass energy allows for customization based on the specific needs and resources of a region.
12. Can biomass energy replace fossil fuels entirely?
While biomass energy has the potential to play a significant role in the transition to renewable energy, it is unlikely to replace fossil fuels entirely. Biomass energy can complement other renewables and contribute to a diversified energy mix. Achieving a sustainable energy future will require a combination of different renewable sources and energy efficiency measures.
Overall, biomass energy holds great promise as a sustainable and renewable energy source that can power communities and contribute to a greener future. Its numerous benefits, from reduced greenhouse gas emissions to job creation and waste management, make it a valuable component of the global energy landscape.
Sources:
- Image Source 1
- Image Source 2
Post a Comment for "how can biomass energy be used"