how does biomass work to produce energy
Question 1: What is biomass?
Biomass refers to organic matter, such as plants or plant-based materials, that can be used as a renewable energy source. It can include wood, agricultural crops, and residues, as well as organic waste.
Comprehensive answer:
- Biomass is a renewable energy source that can be used to produce heat, electricity, or other forms of energy.
- Using biomass as an energy source can help reduce dependence on fossil fuels and decrease greenhouse gas emissions.
- Examples of biomass energy systems include biomass boilers, biogas plants, and biomass power plants.
- Biomass can also be converted into biofuels, such as biodiesel and bioethanol, which can be used as transportation fuels.
- Case study: The use of biomass in Sweden has significantly contributed to the country's renewable energy goals. Sweden has successfully integrated biomass into its energy mix, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and achieving a high degree of energy independence.
Question 2: How does biomass energy work?
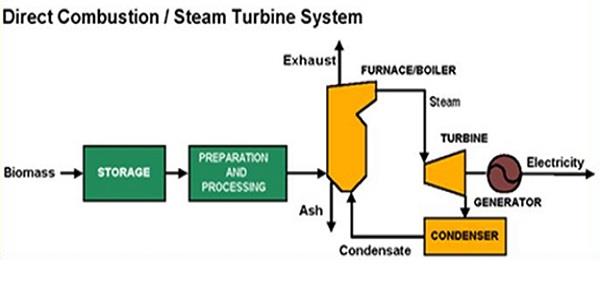
Biomass energy is derived from the conversion of organic matter into usable energy. The process typically involves burning biomass materials to produce heat, which is then used to generate electricity or provide direct heating.
Comprehensive answer:
- Biomass energy generation involves several steps, including biomass collection, preparation, combustion, and energy conversion.
- 1. Biomass collection: Organic materials, such as wood chips, agricultural residues, or dedicated energy crops, are collected.
- 2. Biomass preparation: The collected biomass is then processed to remove impurities and reduce the size of the materials for efficient combustion.
- 3. Combustion: The biomass is burned in a boiler or furnace to produce heat, which can be used directly or converted into other forms of energy.
- 4. Energy conversion: The heat generated from biomass combustion can be used to produce steam, which drives a turbine connected to a generator to produce electricity.
- Case study: The Drax power station in the United Kingdom is a prominent example of biomass energy generation. It has converted several of its coal-fired units to run on biomass pellets, significantly reducing carbon emissions and contributing to renewable energy targets.
Question 3: What are the advantages of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several advantages:
- 1. Renewable and sustainable: Biomass is a renewable energy source as new plant matter can be grown to replace the biomass that is used. It also contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gases.
- 2. Versatile: Biomass can be converted into various energy forms, including heat, electricity, and biofuels.
- 3. Waste reduction: Biomass energy can utilize organic waste materials, reducing the need for landfill space and potentially solving waste management issues.
- 4. Regional energy production: Biomass resources are often available locally, reducing dependence on fossil fuel imports and promoting regional energy self-sufficiency.
- Case study: Denmark has successfully integrated biomass energy into its district heating systems, contributing to its ambitious renewable energy targets. Biomass-fired combined heat and power plants in Denmark provide sustainable and efficient heating to communities.
Question 4: Are there any disadvantages of biomass energy?
While biomass energy has several advantages, there are also some disadvantages to consider:
- 1. Land and water use: Cultivating biomass crops requires land and water resources, which may compete with food production or natural habitats.
- 2. Air pollution: Biomass combustion can release pollutants such as particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, and volatile organic compounds. Proper emission control measures are necessary to minimize air pollution.
- 3. Transport and storage challenges: Biomass materials need to be collected, transported, and stored, which can require significant logistical efforts and infrastructure.
- 4. Intermittency: Biomass energy production may fluctuate depending on the availability of biomass feedstocks, which can affect its reliability as a consistent energy source.
Comprehensive answer:
- Biomass energy has the potential to contribute to sustainable development and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- However, it is crucial to carefully consider the environmental and social impacts associated with biomass production and ensure proper management practices are in place.
- Efforts should be made to minimize land-use conflicts, improve air pollution control technologies, and ensure sustainable biomass sourcing to mitigate potential disadvantages.
Question 5: How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources?
Biomass energy has its advantages and disadvantages compared to other renewable energy sources:
- 1. Biomass vs. Solar Energy: Biomass energy provides continuous power generation, unlike solar energy, which is dependent on sunlight. However, solar energy has lower emissions and requires less land compared to biomass energy.
- 2. Biomass vs. Wind Energy: Biomass energy can provide baseload power, while wind energy is intermittent. However, wind energy has lower emissions and does not require biomass feedstocks.
- 3. Biomass vs. Hydropower: Biomass energy can be produced without the need for large-scale dams and reservoirs, unlike hydropower. However, hydropower has higher power output and can provide reliable and consistent electricity generation.
- 4. Biomass vs. Geothermal Energy: Biomass energy can be more readily available and accessible compared to geothermal energy, which is limited to certain regions. Geothermal energy has lower emissions and provides a continuous source of renewable power.
Comprehensive answer:
- Each renewable energy source has its own unique advantages and limitations, and the choice of energy source depends on various factors such as resource availability, environmental considerations, and energy demands.
- Efforts should be focused on diversifying the energy mix and harnessing multiple renewable energy sources to meet the increasing energy demand while reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Question 6: How can biomass be used for transportation?
Biomass can be converted into biofuels, which can be used as transportation fuels:
- 1. Biodiesel: Biomass, such as vegetable oils or animal fats, can be processed to produce biodiesel, which can be used as a substitute for diesel fuel.
- 2. Bioethanol: Biomass, particularly crops like corn or sugarcane, can be fermented to produce bioethanol, which can be blended with gasoline and used as a fuel in gasoline engines.
- 3. Biogas: Biomass waste materials can be anaerobically digested to produce methane-rich biogas, which can be used as a transportation fuel.
Comprehensive answer:
- Biofuels derived from biomass offer a renewable alternative to fossil fuels in the transportation sector.
- However, it is important to consider the sustainability of biomass feedstocks and ensure that the production of biofuels does not compete with food production or result in negative environmental impacts.
- Research and development efforts are ongoing to improve the efficiency and sustainability of biomass-based biofuels.
Question 7: Can biomass energy be used for residential heating?
Biomass energy can be an effective and sustainable option for residential heating:
- 1. Biomass boilers: Residential buildings can install biomass boilers that burn wood pellets or other biomass materials to provide central heating and hot water.
- 2. Pellet stoves: Biomass pellet stoves are another option for residential heating, providing a renewable and efficient heat source.
- 3. District heating: In some areas, biomass-fired district heating systems supply heat to multiple buildings or communities.
Comprehensive answer:
- Residential biomass heating can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and contribute to lower carbon emissions.
- It is important to consider the availability and sustainability of biomass resources and ensure proper maintenance and operation of biomass heating systems to ensure optimal efficiency and air pollution control.
- Financial incentives and support programs may be available to encourage the adoption of biomass heating in residential buildings.
Question 8: Is biomass energy expensive?
The cost of biomass energy varies depending on factors such as biomass feedstock availability, technology used, and scale of the energy system:
- 1. Biomass availability: The cost of biomass can vary depending on local availability and transportation distance.
- 2. Technology: Different biomass conversion technologies have different capital and operational costs. Advanced technologies may require higher upfront investments but offer greater efficiency and lower operating costs.
- 3. Scale: Large-scale biomass energy projects may benefit from economies of scale, reducing the cost per unit of energy produced.
Comprehensive answer:
- The cost competitiveness of biomass energy depends on various factors and should be evaluated on a case-by-case basis.
- Policy support, incentives, and research and development efforts can further drive down the cost of biomass energy and promote its adoption as a sustainable and cost-effective energy source.
Question 9: Can biomass energy help reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Biomass energy has the potential to contribute to greenhouse gas emissions reduction:
- 1. Carbon neutrality: Biomass is considered carbon-neutral as the carbon dioxide released during biomass combustion is absorbed by plants during their growth, creating a closed carbon cycle.
- 2. Offset for fossil fuels: Biomass energy can replace fossil fuels, which have a higher carbon footprint, thus reducing overall greenhouse gas emissions.
- 3. Waste management: Utilizing biomass for energy can help reduce organic waste and prevent the emission of methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from decaying organic matter.
Comprehensive answer:
- Maximizing the greenhouse gas emissions reduction potential of biomass energy requires sustainable biomass sourcing, efficient energy conversion technologies, and proper emission control measures.
- It is important to consider the lifecycle emissions associated with biomass production and use, including land-use change impacts and indirect emissions related to feedstock sourcing.
- Continued research and development efforts are essential to further improve the environmental performance of biomass energy systems.
Question 10: Can biomass energy be used in developing countries?
Biomass energy can be particularly relevant and beneficial in developing countries:
- 1. Local resource availability: Developing countries often have abundant biomass resources, making biomass energy a readily available and cost-effective option.
- 2. Energy access: Biomass energy can help provide clean and affordable energy access to rural communities that may not have access to grid electricity.
- 3. Job creation: Utilizing biomass resources for energy production can create employment opportunities in rural areas, contributing to local economic development.
Comprehensive answer:
- Deploying biomass energy in developing countries requires proper planning, infrastructure development, and capacity building.
- It is essential to ensure sustainable biomass sourcing, minimize environmental and social impacts, and promote inclusive and participatory approaches in biomass energy projects.
- International cooperation and financial support can play a crucial role in facilitating the adoption of biomass energy in developing countries.
Question 11: Can biomass energy reduce dependence on fossil fuels?
Biomass energy has the potential to reduce dependence on fossil fuels:
- 1. Energy diversification: Incorporating biomass energy into the energy mix provides an alternative to fossil fuels, reducing reliance on finite and environmentally damaging resources.
- 2. Baseload power: Biomass energy can provide baseload power generation, complementing intermittent renewable energy sources like wind and solar power.
- 3. National energy security: Utilizing domestically available biomass resources can enhance energy self-sufficiency and reduce dependence on fossil fuel imports.
Comprehensive answer:
- Policies and incentives that promote biomass energy deployment, research and development of advanced biomass conversion technologies, and sustainable biomass sourcing can accelerate the transition to a more sustainable and diversified energy system less dependent on fossil fuels.
- The integration of biomass energy with other renewable energy sources is crucial for achieving long-term energy security and sustainability goals.
Question 12: Are there any government incentives for biomass energy?
Many governments offer incentives and support programs to promote the adoption of biomass energy:
- 1. Feed-in tariffs: Governments may provide a fixed payment for each unit of electricity produced from biomass, encouraging biomass energy generation.
- 2. Tax incentives: Tax credits or exemptions may be available for investments in biomass energy projects or the purchase of biomass heating systems.
- 3. Grants and subsidies: Governments may provide financial support, grants, or subsidies for the development and implementation of biomass energy projects.
- 4. Renewable energy targets: Governments often set renewable energy targets, which create a favorable environment for biomass energy development and investment.
Comprehensive answer:
- Government incentives play a crucial role in scaling up biomass energy deployment and making it economically viable.
- Policy stability, transparency, and long-term planning are essential to provide certainty for biomass energy investors and developers.
- Continuous monitoring and evaluation of incentive programs are necessary to ensure their effectiveness and address any potential unintended consequences.

Post a Comment for "how does biomass work to produce energy"