Advantages of Biogas - PluginIndia
What's Biomass Energy and How Can it Benefit You? | financeguru.com

Common Questions about Biogas and Biomass Energy
1. What is biogas and how is it produced?

Biogas is a type of renewable energy that is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion. It is composed primarily of methane gas and carbon dioxide, along with trace amounts of other gases. The production of biogas involves breaking down organic materials, such as agricultural waste, animal manure, or food waste, in an oxygen-free environment. The organic matter is consumed by bacteria, which release methane as a byproduct. Benefits of biogas production include: - Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions - Waste management and odor control - Generation of renewable energy - Production of nutrient-rich digestate that can be used as fertilizer 2. How is biomass energy different from biogas?

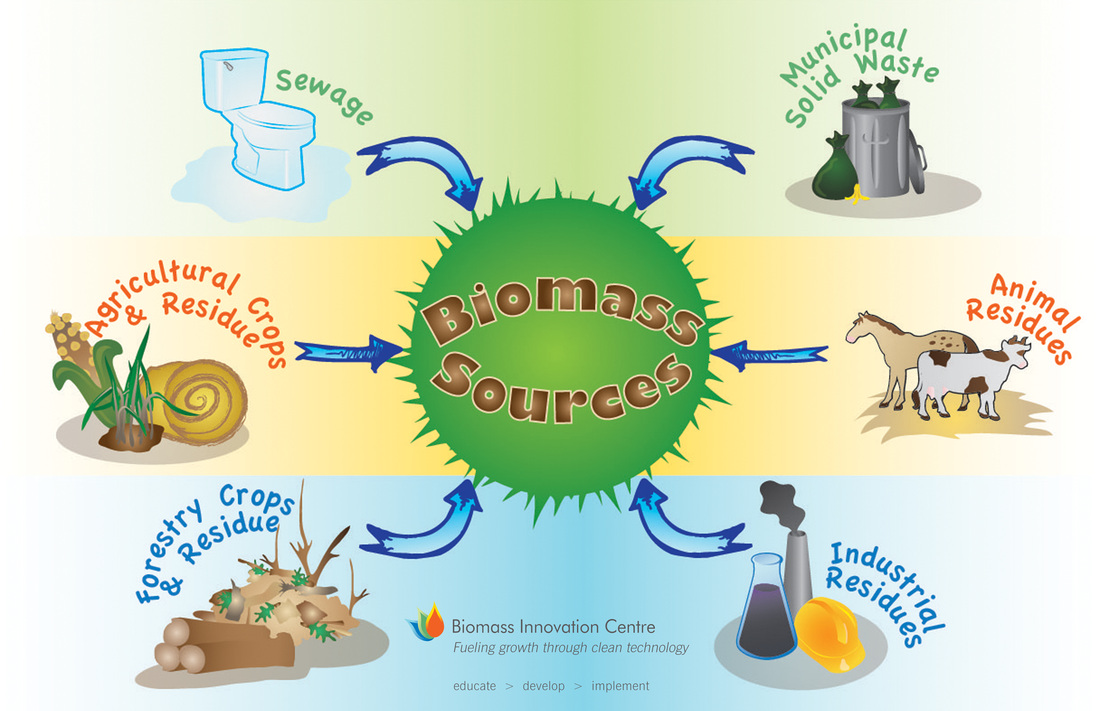
Biomass energy refers to the use of organic matter, such as wood, crop residues, or dedicated energy crops, as a fuel source to generate heat or electricity. It can be produced through various processes, including combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion. Biogas, on the other hand, specifically refers to the gas produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While both biomass energy and biogas are forms of renewable energy, biogas is a subset of biomass energy. Key differences between biomass energy and biogas include: - Biomass energy can be derived from a wider range of organic materials, while biogas is primarily produced from organic waste. - Biomass energy can be produced through different conversion processes, such as combustion or gasification, while biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion. 3. What are the advantages of using biogas as a renewable energy source? Using biogas as a renewable energy source offers several benefits: - Reduces dependence on fossil fuels: Biogas provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing the carbon footprint and dependence on imported energy. - Mitigates greenhouse gas emissions: The process of anaerobic digestion used to produce biogas captures and converts methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into a usable energy source, thereby reducing emissions. - Efficient waste management: Biogas production allows for the proper disposal and treatment of organic waste materials, reducing pollution and odor problems associated with landfills and animal manure. - Generates decentralized energy: Biogas can be produced on a smaller scale, which enables decentralized energy production and increases energy security. - Provides nutrient-rich byproducts: The digestate produced during the biogas production process can be used as a high-quality organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture practices. 4. Is biogas production economically viable? Biogas production can be economically viable under certain conditions. The profitability of biogas projects depends on factors such as the availability and cost of feedstock, government incentives, electricity prices, and the efficiency of the biogas plant. Additionally, economic viability can be enhanced through the utilization of byproducts, such as the generation of heat or the sale of digestate as fertilizer. 5. How can biogas be used for cooking and heating? Biogas can be used as a direct fuel for cooking and heating purposes. It can replace traditional fuels, such as firewood or LPG (liquefied petroleum gas), in household stoves or cooking appliances. Biogas can also be used in decentralized heating systems for space heating or water heating in residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. The utilization of biogas for cooking and heating purposes provides a sustainable and clean energy alternative. 6. Can biogas be used to generate electricity? Yes, biogas can be used to generate electricity through a process called combined heat and power (CHP) or cogeneration. In a CHP system, biogas is combusted in an engine or turbine to produce mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity. The heat generated during this process can also be captured and used for heating purposes, increasing overall energy efficiency. Biogas-based electricity generation provides a renewable energy source that can be integrated into the grid or used off-grid in remote areas. 7. What are the limitations or challenges of biogas production? Some of the challenges and limitations of biogas production include: - Availability and quality of feedstock: The availability and consistency of organic waste materials suitable for biogas production can vary, and the quality of the feedstock affects the efficiency and performance of the biogas plant. - Capital investment and operational costs: The initial investment required to establish a biogas plant, as well as the ongoing operational and maintenance costs, can be significant. - Regulatory and policy support: The implementation and growth of biogas projects can be influenced by policies, regulations, and government incentives or subsidies. - Technical complexities: The design, construction, and operation of biogas plants require specialized knowledge and expertise. Issues such as process control, gas purification, and digestate management can pose technical challenges. - Market demand and revenue streams: The economic viability of biogas projects depends on the availability of markets for the produced biogas or its byproducts, such as electricity, heat, or digestate. 8. Can biogas production help reduce greenhouse gas emissions? Yes, biogas production can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When organic waste decomposes in landfills or untreated manure is stored, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. By capturing and utilizing the methane through anaerobic digestion, biogas production prevents its release into the atmosphere, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the combustion of biogas as a fuel source produces carbon dioxide, which has a lower impact on climate change compared to methane. 9. What are the environmental benefits of biomass energy and biogas? Biomass energy and biogas production offer several environmental benefits, including: - Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: By using organic waste materials or dedicated energy crops as fuel sources, biomass energy and biogas production contribute to the reduction of fossil fuel consumption and associated environmental impacts. - Lower greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy and biogas production help mitigate climate change by replacing fossil fuels that release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Additionally, biogas production prevents the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. - Waste management and pollution reduction: Biomass energy and biogas production provide a sustainable solution for managing organic waste materials, reducing pollution, and improving air and water quality. - Soil fertility and sustainable agriculture: The digestate produced during biogas production can be used as organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. 10. Can biomass energy and biogas production be integrated into existing energy systems? Yes, biomass energy and biogas production can be integrated into existing energy systems. Biomass energy can be used as a direct replacement for fossil fuels in existing combustion-based power plants or heating systems, with some modifications to accommodate the specific fuel characteristics. Biogas production can be integrated into anaerobic digesters at wastewater treatment plants, farms, or other organic waste processing facilities. The generated biogas can be used to produce heat, electricity, or transportation fuels, depending on the specific needs of the system. 11. Are there any technological advancements in biogas and biomass energy production? Technological advancements in biogas and biomass energy production are continually being made to improve efficiency, increase resource utilization, and reduce costs. Some of these advancements include: - Advanced anaerobic digestion processes: Research and development efforts are focused on improving anaerobic digestion technologies, such as high-rate systems, thermophilic digestion, or two-stage digestion, to enhance gas production rates and stability. - Gas upgrading and purification: Advanced gas upgrading techniques, such as pressure swing adsorption or membrane separation, are being developed to remove impurities and increase the methane content of biogas, making it suitable for injection into natural gas pipelines or use as a transportation fuel. - Co-digestion and feedstock flexibility: The ability to co-digest multiple feedstocks, such as agricultural residues, energy crops, or food waste, increases biogas production potential and enhances the overall sustainability of the process. - Integration with other renewable energy technologies: Biomass energy and biogas production can be integrated with other renewable energy technologies, such as solar or wind power, to create hybrid energy systems that provide a more stable and consistent energy supply. 12. Are there any success stories or case studies related to biogas and biomass energy? There are numerous success stories and case studies showcasing the benefits and applications of biogas and biomass energy. Some examples include: - The city of Stockholm, Sweden, has implemented a successful biogas production program, utilizing organic waste from households, restaurants, and wastewater treatment plants. The produced biogas is used as a transportation fuel for buses and waste collection vehicles, reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. - The state of California in the United States has implemented various policies and incentives to promote biogas and biomass energy production. This has led to the establishment of numerous biogas plants on dairy farms, which not only generate renewable electricity but also help manage animal waste and reduce methane emissions. - The Drax Power Station in the United Kingdom has converted several of its coal-fired units to burn biomass pellets made from sustainably sourced wood. This biomass conversion has significantly reduced greenhouse gas emissions from the power plant and contributed to the country's renewable energy goals. In conclusion, biogas and biomass energy offer significant advantages as renewable energy sources. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions, provide sustainable waste management solutions, and contribute to energy independence. Technological advancements and successful case studies demonstrate the potential and effectiveness of these energy sources in mitigating climate change and promoting a more sustainable future.


 Biogas is a type of renewable energy that is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion. It is composed primarily of methane gas and carbon dioxide, along with trace amounts of other gases. The production of biogas involves breaking down organic materials, such as agricultural waste, animal manure, or food waste, in an oxygen-free environment. The organic matter is consumed by bacteria, which release methane as a byproduct. Benefits of biogas production include: - Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions - Waste management and odor control - Generation of renewable energy - Production of nutrient-rich digestate that can be used as fertilizer 2. How is biomass energy different from biogas?
Biogas is a type of renewable energy that is produced through the process of anaerobic digestion. It is composed primarily of methane gas and carbon dioxide, along with trace amounts of other gases. The production of biogas involves breaking down organic materials, such as agricultural waste, animal manure, or food waste, in an oxygen-free environment. The organic matter is consumed by bacteria, which release methane as a byproduct. Benefits of biogas production include: - Reduction of greenhouse gas emissions - Waste management and odor control - Generation of renewable energy - Production of nutrient-rich digestate that can be used as fertilizer 2. How is biomass energy different from biogas?  Biomass energy refers to the use of organic matter, such as wood, crop residues, or dedicated energy crops, as a fuel source to generate heat or electricity. It can be produced through various processes, including combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion. Biogas, on the other hand, specifically refers to the gas produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While both biomass energy and biogas are forms of renewable energy, biogas is a subset of biomass energy. Key differences between biomass energy and biogas include: - Biomass energy can be derived from a wider range of organic materials, while biogas is primarily produced from organic waste. - Biomass energy can be produced through different conversion processes, such as combustion or gasification, while biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion. 3. What are the advantages of using biogas as a renewable energy source? Using biogas as a renewable energy source offers several benefits: - Reduces dependence on fossil fuels: Biogas provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing the carbon footprint and dependence on imported energy. - Mitigates greenhouse gas emissions: The process of anaerobic digestion used to produce biogas captures and converts methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into a usable energy source, thereby reducing emissions. - Efficient waste management: Biogas production allows for the proper disposal and treatment of organic waste materials, reducing pollution and odor problems associated with landfills and animal manure. - Generates decentralized energy: Biogas can be produced on a smaller scale, which enables decentralized energy production and increases energy security. - Provides nutrient-rich byproducts: The digestate produced during the biogas production process can be used as a high-quality organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture practices. 4. Is biogas production economically viable? Biogas production can be economically viable under certain conditions. The profitability of biogas projects depends on factors such as the availability and cost of feedstock, government incentives, electricity prices, and the efficiency of the biogas plant. Additionally, economic viability can be enhanced through the utilization of byproducts, such as the generation of heat or the sale of digestate as fertilizer. 5. How can biogas be used for cooking and heating? Biogas can be used as a direct fuel for cooking and heating purposes. It can replace traditional fuels, such as firewood or LPG (liquefied petroleum gas), in household stoves or cooking appliances. Biogas can also be used in decentralized heating systems for space heating or water heating in residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. The utilization of biogas for cooking and heating purposes provides a sustainable and clean energy alternative. 6. Can biogas be used to generate electricity? Yes, biogas can be used to generate electricity through a process called combined heat and power (CHP) or cogeneration. In a CHP system, biogas is combusted in an engine or turbine to produce mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity. The heat generated during this process can also be captured and used for heating purposes, increasing overall energy efficiency. Biogas-based electricity generation provides a renewable energy source that can be integrated into the grid or used off-grid in remote areas. 7. What are the limitations or challenges of biogas production? Some of the challenges and limitations of biogas production include: - Availability and quality of feedstock: The availability and consistency of organic waste materials suitable for biogas production can vary, and the quality of the feedstock affects the efficiency and performance of the biogas plant. - Capital investment and operational costs: The initial investment required to establish a biogas plant, as well as the ongoing operational and maintenance costs, can be significant. - Regulatory and policy support: The implementation and growth of biogas projects can be influenced by policies, regulations, and government incentives or subsidies. - Technical complexities: The design, construction, and operation of biogas plants require specialized knowledge and expertise. Issues such as process control, gas purification, and digestate management can pose technical challenges. - Market demand and revenue streams: The economic viability of biogas projects depends on the availability of markets for the produced biogas or its byproducts, such as electricity, heat, or digestate. 8. Can biogas production help reduce greenhouse gas emissions? Yes, biogas production can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When organic waste decomposes in landfills or untreated manure is stored, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. By capturing and utilizing the methane through anaerobic digestion, biogas production prevents its release into the atmosphere, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the combustion of biogas as a fuel source produces carbon dioxide, which has a lower impact on climate change compared to methane. 9. What are the environmental benefits of biomass energy and biogas? Biomass energy and biogas production offer several environmental benefits, including: - Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: By using organic waste materials or dedicated energy crops as fuel sources, biomass energy and biogas production contribute to the reduction of fossil fuel consumption and associated environmental impacts. - Lower greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy and biogas production help mitigate climate change by replacing fossil fuels that release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Additionally, biogas production prevents the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. - Waste management and pollution reduction: Biomass energy and biogas production provide a sustainable solution for managing organic waste materials, reducing pollution, and improving air and water quality. - Soil fertility and sustainable agriculture: The digestate produced during biogas production can be used as organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. 10. Can biomass energy and biogas production be integrated into existing energy systems? Yes, biomass energy and biogas production can be integrated into existing energy systems. Biomass energy can be used as a direct replacement for fossil fuels in existing combustion-based power plants or heating systems, with some modifications to accommodate the specific fuel characteristics. Biogas production can be integrated into anaerobic digesters at wastewater treatment plants, farms, or other organic waste processing facilities. The generated biogas can be used to produce heat, electricity, or transportation fuels, depending on the specific needs of the system. 11. Are there any technological advancements in biogas and biomass energy production? Technological advancements in biogas and biomass energy production are continually being made to improve efficiency, increase resource utilization, and reduce costs. Some of these advancements include: - Advanced anaerobic digestion processes: Research and development efforts are focused on improving anaerobic digestion technologies, such as high-rate systems, thermophilic digestion, or two-stage digestion, to enhance gas production rates and stability. - Gas upgrading and purification: Advanced gas upgrading techniques, such as pressure swing adsorption or membrane separation, are being developed to remove impurities and increase the methane content of biogas, making it suitable for injection into natural gas pipelines or use as a transportation fuel. - Co-digestion and feedstock flexibility: The ability to co-digest multiple feedstocks, such as agricultural residues, energy crops, or food waste, increases biogas production potential and enhances the overall sustainability of the process. - Integration with other renewable energy technologies: Biomass energy and biogas production can be integrated with other renewable energy technologies, such as solar or wind power, to create hybrid energy systems that provide a more stable and consistent energy supply. 12. Are there any success stories or case studies related to biogas and biomass energy? There are numerous success stories and case studies showcasing the benefits and applications of biogas and biomass energy. Some examples include: - The city of Stockholm, Sweden, has implemented a successful biogas production program, utilizing organic waste from households, restaurants, and wastewater treatment plants. The produced biogas is used as a transportation fuel for buses and waste collection vehicles, reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. - The state of California in the United States has implemented various policies and incentives to promote biogas and biomass energy production. This has led to the establishment of numerous biogas plants on dairy farms, which not only generate renewable electricity but also help manage animal waste and reduce methane emissions. - The Drax Power Station in the United Kingdom has converted several of its coal-fired units to burn biomass pellets made from sustainably sourced wood. This biomass conversion has significantly reduced greenhouse gas emissions from the power plant and contributed to the country's renewable energy goals. In conclusion, biogas and biomass energy offer significant advantages as renewable energy sources. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions, provide sustainable waste management solutions, and contribute to energy independence. Technological advancements and successful case studies demonstrate the potential and effectiveness of these energy sources in mitigating climate change and promoting a more sustainable future.
Biomass energy refers to the use of organic matter, such as wood, crop residues, or dedicated energy crops, as a fuel source to generate heat or electricity. It can be produced through various processes, including combustion, gasification, or anaerobic digestion. Biogas, on the other hand, specifically refers to the gas produced through the anaerobic digestion of organic waste. While both biomass energy and biogas are forms of renewable energy, biogas is a subset of biomass energy. Key differences between biomass energy and biogas include: - Biomass energy can be derived from a wider range of organic materials, while biogas is primarily produced from organic waste. - Biomass energy can be produced through different conversion processes, such as combustion or gasification, while biogas is produced through anaerobic digestion. 3. What are the advantages of using biogas as a renewable energy source? Using biogas as a renewable energy source offers several benefits: - Reduces dependence on fossil fuels: Biogas provides a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels, reducing the carbon footprint and dependence on imported energy. - Mitigates greenhouse gas emissions: The process of anaerobic digestion used to produce biogas captures and converts methane, a potent greenhouse gas, into a usable energy source, thereby reducing emissions. - Efficient waste management: Biogas production allows for the proper disposal and treatment of organic waste materials, reducing pollution and odor problems associated with landfills and animal manure. - Generates decentralized energy: Biogas can be produced on a smaller scale, which enables decentralized energy production and increases energy security. - Provides nutrient-rich byproducts: The digestate produced during the biogas production process can be used as a high-quality organic fertilizer, promoting sustainable agriculture practices. 4. Is biogas production economically viable? Biogas production can be economically viable under certain conditions. The profitability of biogas projects depends on factors such as the availability and cost of feedstock, government incentives, electricity prices, and the efficiency of the biogas plant. Additionally, economic viability can be enhanced through the utilization of byproducts, such as the generation of heat or the sale of digestate as fertilizer. 5. How can biogas be used for cooking and heating? Biogas can be used as a direct fuel for cooking and heating purposes. It can replace traditional fuels, such as firewood or LPG (liquefied petroleum gas), in household stoves or cooking appliances. Biogas can also be used in decentralized heating systems for space heating or water heating in residential, commercial, or industrial buildings. The utilization of biogas for cooking and heating purposes provides a sustainable and clean energy alternative. 6. Can biogas be used to generate electricity? Yes, biogas can be used to generate electricity through a process called combined heat and power (CHP) or cogeneration. In a CHP system, biogas is combusted in an engine or turbine to produce mechanical energy, which is then converted into electricity. The heat generated during this process can also be captured and used for heating purposes, increasing overall energy efficiency. Biogas-based electricity generation provides a renewable energy source that can be integrated into the grid or used off-grid in remote areas. 7. What are the limitations or challenges of biogas production? Some of the challenges and limitations of biogas production include: - Availability and quality of feedstock: The availability and consistency of organic waste materials suitable for biogas production can vary, and the quality of the feedstock affects the efficiency and performance of the biogas plant. - Capital investment and operational costs: The initial investment required to establish a biogas plant, as well as the ongoing operational and maintenance costs, can be significant. - Regulatory and policy support: The implementation and growth of biogas projects can be influenced by policies, regulations, and government incentives or subsidies. - Technical complexities: The design, construction, and operation of biogas plants require specialized knowledge and expertise. Issues such as process control, gas purification, and digestate management can pose technical challenges. - Market demand and revenue streams: The economic viability of biogas projects depends on the availability of markets for the produced biogas or its byproducts, such as electricity, heat, or digestate. 8. Can biogas production help reduce greenhouse gas emissions? Yes, biogas production can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions. When organic waste decomposes in landfills or untreated manure is stored, it releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas with a much higher global warming potential than carbon dioxide. By capturing and utilizing the methane through anaerobic digestion, biogas production prevents its release into the atmosphere, thereby reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the combustion of biogas as a fuel source produces carbon dioxide, which has a lower impact on climate change compared to methane. 9. What are the environmental benefits of biomass energy and biogas? Biomass energy and biogas production offer several environmental benefits, including: - Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: By using organic waste materials or dedicated energy crops as fuel sources, biomass energy and biogas production contribute to the reduction of fossil fuel consumption and associated environmental impacts. - Lower greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass energy and biogas production help mitigate climate change by replacing fossil fuels that release carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Additionally, biogas production prevents the release of methane, a potent greenhouse gas. - Waste management and pollution reduction: Biomass energy and biogas production provide a sustainable solution for managing organic waste materials, reducing pollution, and improving air and water quality. - Soil fertility and sustainable agriculture: The digestate produced during biogas production can be used as organic fertilizer, enhancing soil fertility and promoting sustainable agricultural practices. 10. Can biomass energy and biogas production be integrated into existing energy systems? Yes, biomass energy and biogas production can be integrated into existing energy systems. Biomass energy can be used as a direct replacement for fossil fuels in existing combustion-based power plants or heating systems, with some modifications to accommodate the specific fuel characteristics. Biogas production can be integrated into anaerobic digesters at wastewater treatment plants, farms, or other organic waste processing facilities. The generated biogas can be used to produce heat, electricity, or transportation fuels, depending on the specific needs of the system. 11. Are there any technological advancements in biogas and biomass energy production? Technological advancements in biogas and biomass energy production are continually being made to improve efficiency, increase resource utilization, and reduce costs. Some of these advancements include: - Advanced anaerobic digestion processes: Research and development efforts are focused on improving anaerobic digestion technologies, such as high-rate systems, thermophilic digestion, or two-stage digestion, to enhance gas production rates and stability. - Gas upgrading and purification: Advanced gas upgrading techniques, such as pressure swing adsorption or membrane separation, are being developed to remove impurities and increase the methane content of biogas, making it suitable for injection into natural gas pipelines or use as a transportation fuel. - Co-digestion and feedstock flexibility: The ability to co-digest multiple feedstocks, such as agricultural residues, energy crops, or food waste, increases biogas production potential and enhances the overall sustainability of the process. - Integration with other renewable energy technologies: Biomass energy and biogas production can be integrated with other renewable energy technologies, such as solar or wind power, to create hybrid energy systems that provide a more stable and consistent energy supply. 12. Are there any success stories or case studies related to biogas and biomass energy? There are numerous success stories and case studies showcasing the benefits and applications of biogas and biomass energy. Some examples include: - The city of Stockholm, Sweden, has implemented a successful biogas production program, utilizing organic waste from households, restaurants, and wastewater treatment plants. The produced biogas is used as a transportation fuel for buses and waste collection vehicles, reducing emissions and dependence on fossil fuels. - The state of California in the United States has implemented various policies and incentives to promote biogas and biomass energy production. This has led to the establishment of numerous biogas plants on dairy farms, which not only generate renewable electricity but also help manage animal waste and reduce methane emissions. - The Drax Power Station in the United Kingdom has converted several of its coal-fired units to burn biomass pellets made from sustainably sourced wood. This biomass conversion has significantly reduced greenhouse gas emissions from the power plant and contributed to the country's renewable energy goals. In conclusion, biogas and biomass energy offer significant advantages as renewable energy sources. They reduce greenhouse gas emissions, provide sustainable waste management solutions, and contribute to energy independence. Technological advancements and successful case studies demonstrate the potential and effectiveness of these energy sources in mitigating climate change and promoting a more sustainable future.
Post a Comment for "how can biomass be used as a source of energy"