how does biomass energy produce electricity
Why is biomass used for electricity generation?
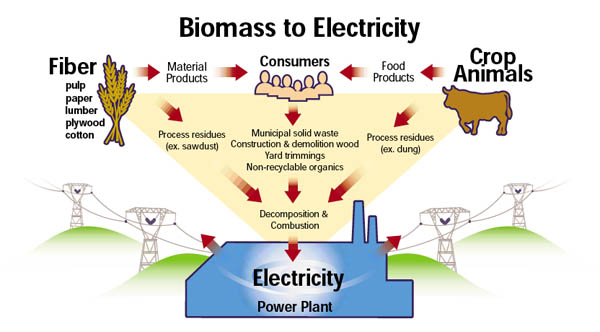
Biomass is used for electricity generation due to several reasons:
- Biomass is a renewable energy source that comes from organic materials, such as wood, crops, and agricultural residues. It is readily available and can be replenished over time.
- It helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions as biomass emits fewer carbon dioxide emissions compared to fossil fuels.
- Biomass power plants can be flexible in terms of fuel sources and can utilize various biomass feedstocks, providing a diversified energy supply.
- Using biomass for electricity generation contributes to waste management by utilizing organic materials that would otherwise go to landfills.
- It promotes local economic development by creating jobs in the biomass supply chain, including harvesting, processing, and transportation.
How is biomass used to generate electricity?

Biomass is utilized to generate electricity through the following process:
- Feedstock collection: Organic materials, such as wood chips, agricultural residues, or energy crops, are collected and transported to the biomass power plant.
- Combustion: The biomass feedstock is burned in a boiler, producing heat energy.
- Steam generation: The heat energy is used to generate steam, which drives a steam turbine.
- Electricity generation: The steam turbine is connected to a generator, which produces electricity.
- Distribution: The generated electricity is then distributed through the power grid to consumers.
What are the advantages of biomass for electricity generation?
Using biomass for electricity generation offers several advantages:
- Renewable energy source: Biomass is derived from organic materials, which can be regrown or replenished over time.
- Reduces greenhouse gas emissions: Biomass combustion releases carbon dioxide, but since the feedstock absorbs carbon dioxide during its growth, it is considered to be carbon-neutral or low carbon.
- Diversifies energy supply: Biomass can be sourced from various feedstocks, providing a diversified energy mix and reducing dependence on fossil fuels.
- Utilizes waste materials: By using agricultural residues and other organic waste materials, biomass power generation contributes to waste management and minimizes landfill usage.
Is biomass a sustainable energy source?
Yes, biomass is considered a sustainable energy source. Here's why:
- Renewable nature: Biomass is derived from organic materials that can be continuously replenished over time through sustainable practices, such as reforestation and crop rotation.
- Carbon neutrality: Although burning biomass releases carbon dioxide, the emissions are considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by the biomass feedstock during growth.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuels: Utilizing biomass for electricity generation helps reduce the dependency on finite fossil fuel reserves, promoting sustainable energy practices.
- Local economic benefits: Biomass power plants often source their feedstock locally, which creates job opportunities in the biomass supply chain, supporting local economies.
What are the challenges of biomass for electricity generation?
While biomass offers several advantages, there are also some challenges associated with its use for electricity generation:
- Feedstock availability and logistics: Ensuring a consistent and reliable supply of biomass feedstock can be a challenge, as it often depends on seasonal factors and availability of the organic materials.
- Energy density: Biomass generally has a lower energy density compared to fossil fuels, which means a larger volume of biomass is required to generate the same amount of energy.
- Emissions and air quality concerns: Although biomass is considered carbon-neutral, its combustion can still release air pollutants, such as particulate matter and nitrogen oxides, which need to be managed through advanced emission control technologies.
- Land use impact: Scaling up biomass production for electricity generation may require significant land resources, potentially competing with other land uses, such as food production or biodiversity conservation.
What are some examples of biomass used for electricity generation?
Biomass for electricity generation can be sourced from various materials, including:
- Wood chips and pellets derived from forestry residues and sustainable timber harvesting practices.
- Agricultural residues, such as corn stalks, rice husks, and sugarcane bagasse.
- Energy crops specifically grown for biomass energy production, such as switchgrass and miscanthus.
- Organic waste materials, including landfill gas and sewage sludge.
How does biomass compare to other renewable energy sources?
When compared to other renewable energy sources, biomass has its unique advantages and considerations:
- Biomass vs. Solar Energy: While solar energy is abundant and directly converts sunlight into electricity, biomass provides a reliable, dispatchable energy source that can operate regardless of weather conditions or time of day.
- Biomass vs. Wind Energy: Wind energy is also intermittent and subject to variations in wind speed, making it complemented by the stable, continuous supply of electricity from biomass power plants.
- Biomass vs. Hydropower: Hydropower relies on water flow, while biomass is not dependent on a specific geographical location, making it more universally applicable.
- Biomass vs. Geothermal Energy: Geothermal energy harnesses heat from the Earth's core, while biomass utilizes organic materials, offering different pathways for renewable electricity generation.
What are some potential future developments in biomass electricity generation?
The future of biomass electricity generation holds several potential developments:
- Advanced Conversion Technologies: Ongoing research focuses on developing more efficient and cleaner biomass conversion technologies, such as gasification and pyrolysis, which can achieve higher energy conversion efficiencies and reduce emissions.
- Co-firing with Fossil Fuels: Co-firing biomass with fossil fuels in existing power plants can help reduce carbon emissions while making use of existing infrastructure. However, careful consideration is necessary to ensure sustainable biomass sourcing.
- Bioenergy with Carbon Capture and Storage (BECCS): Integrated BECCS systems can capture the carbon dioxide emissions from biomass combustion and store it underground, resulting in negative emissions and helping to mitigate climate change.
- Biomass from Algae: Research is being conducted on utilizing algae as a biomass feedstock, offering the potential for sustainable and high-yielding biomass production without competing with agricultural land.
What are the economic benefits of biomass electricity generation?
Biomass electricity generation can have several economic benefits:
- Job Creation: The biomass industry creates jobs across the entire supply chain, including feedstock collection, transportation, processing, and power plant operation, contributing to local and regional economic development.
- Community Revenue: Biomass power plants can provide a stable source of revenue for rural communities by purchasing biomass feedstock locally and contributing to the tax base.
- Energy Independence: By diversifying the energy supply with biomass, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels, improving energy security and potentially saving on foreign currency expenditures.
- Green Investment Opportunities: The growth of the biomass industry creates investment opportunities in research, development, and deployment of advanced biomass conversion technologies.
How does biomass electricity generation contribute to environmental sustainability?
Biomass electricity generation contributes to environmental sustainability in the following ways:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass is considered a low carbon or carbon-neutral energy source since the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed during biomass growth.
- Waste Reduction: Biomass power plants utilize organic waste materials, such as agricultural residues and forestry by-products, diverting them from landfills and reducing methane emissions.
- Local Air Quality Improvement: Advanced emission control technologies in biomass power plants reduce the release of pollutants and particulate matter, contributing to improved air quality compared to some fossil fuel combustion.
- Conservation of Natural Resources: By relying on organic materials, biomass electricity generation reduces the consumption of finite fossil fuel reserves and helps preserve natural resources for future generations.
What role does biomass electricity generation play in a sustainable energy transition?
In a sustainable energy transition, biomass electricity generation plays the following roles:
- Renewable Energy Diversification: Biomass adds a diverse renewable energy source to the energy mix, alongside other renewables like solar, wind, and hydropower, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Grid Stabilization: Biomass power plants can provide stable, dispatchable electricity, helping balance the intermittent nature of other renewables and supporting a reliable power grid.
- Regional Energy Independence: Biomass feedstocks can be locally sourced, enhancing energy security by reducing dependence on external energy sources and promoting decentralized energy generation.
- Transition Support for Fossil Fuel-Dependent Regions: Biomass power plants can be integrated into regions heavily reliant on fossil fuel industries, providing a transition pathway and supporting the local economy.
Post a Comment for "how does biomass energy produce electricity"