how can biomass be used as an energy source
Advantages of Biogas
Biogas is a renewable energy source that is gaining popularity due to its numerous advantages. Let's explore some common questions people have about biogas and its benefits:
1. What is biogas?
Biogas is a type of gas produced from the decomposition of organic matter in the absence of oxygen. It is primarily composed of methane and carbon dioxide.
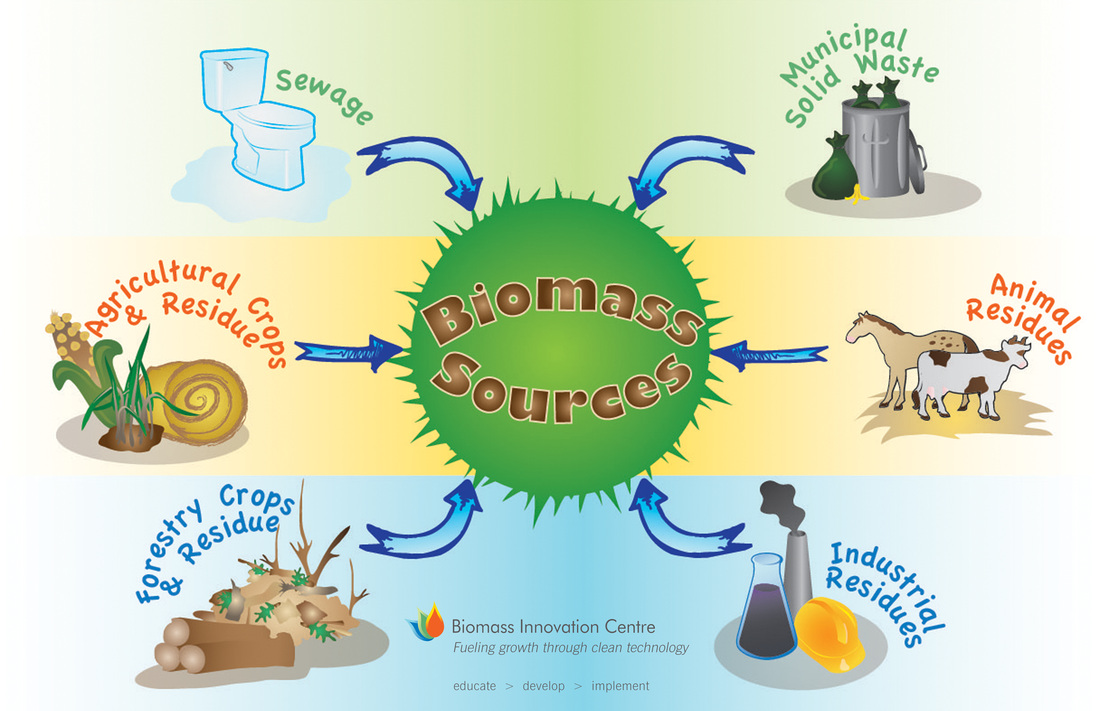
2. How is biogas produced?
Biogas is produced through a process called anaerobic digestion. Organic materials such as agricultural waste, food waste, and sewage sludge are broken down by bacteria in an oxygen-free environment, resulting in the production of biogas.
3. What are the environmental benefits of biogas?
Biogas offers several environmental benefits, including:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Biogas production helps to mitigate climate change by capturing methane, a potent greenhouse gas, from organic waste.
- Renewable energy source: Biogas is a renewable energy source that can replace fossil fuels, reducing dependence on non-renewable resources.
- Waste management solution: Biogas production provides a sustainable solution for managing organic waste, reducing landfill waste and associated environmental issues.
4. How can biogas be used?
Biogas can be used for various purposes, including:
- Electricity generation: Biogas can be utilized in gas engines or turbines to produce electricity.
- Heat generation: Biogas can be combusted directly to generate heat for cooking, heating, or industrial processes.
- Transportation fuel: Biogas can be purified and upgraded to biomethane, which can be used as a renewable fuel for vehicles.
5. What are the economic benefits of biogas?
The economic benefits of biogas include:
- Cost savings: Biogas production can help reduce energy costs for households, farms, and industries.
- Revenue generation: Biogas plants can generate revenue by selling excess electricity or biomethane to the grid or local communities.
- Job creation: The biogas industry creates employment opportunities in areas such as plant operation, maintenance, and feedstock supply.
6. Are there any challenges associated with biogas production?
While biogas production offers numerous benefits, there are some challenges to consider:
- Feedstock availability: Adequate and consistent feedstock supply is essential for efficient biogas production.
- Technology and infrastructure: Biogas production requires suitable technology and infrastructure, which may require initial investment.
- Digestate management: The byproduct of biogas production, known as digestate, needs to be managed properly to avoid environmental impacts.
7. Can biogas improve energy independence?
Yes, biogas can contribute to energy independence by providing a local and renewable energy source. It reduces dependence on imported fossil fuels and promotes self-sufficiency in energy generation.
8. Is biogas production scalable?
Biogas production is scalable and can be tailored to suit different needs and sizes. From small-scale household digesters to large-scale industrial plants, biogas production can be adapted to varying requirements.
9. Does biogas production have any impact on agriculture?
Biogas production can have positive impacts on agriculture, such as:
- Nutrient recycling: The digestate generated during biogas production can be used as an organic fertilizer, enriching soil fertility.
- Reduced odor and pathogens: Anaerobic digestion of agricultural waste can help reduce odor and destroy harmful pathogens, improving local environmental conditions.
10. Can biogas help reduce carbon emissions?
Yes, biogas production plays a significant role in reducing carbon emissions. By capturing methane from organic waste and utilizing it as a fuel source, biogas helps to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating climate change.
11. What are the social benefits of biogas?
Biogas production offers several social benefits, including:
- Improved sanitation: The use of biogas systems for sewage treatment improves sanitation conditions in communities, particularly in rural areas.
- Health benefits: Biogas reduces indoor air pollution by replacing traditional cooking fuels, such as wood or charcoal, with cleaner-burning biogas.
- Community development: Biogas projects can contribute to the development of local communities, creating employment opportunities and improving quality of life.
12. How can individuals contribute to biogas production?
Individuals can contribute to biogas production by:
- Separating organic waste: Properly segregating food waste and other organic materials for biogas production can enhance feedstock availability.
- Supporting local projects: Encouraging and supporting local biogas projects, such as community digesters or decentralized systems, can promote the adoption of biogas on a smaller scale.
- Advocating for renewable energy: Raising awareness about the benefits of biogas and advocating for renewable energy policies can create a positive impact.
Overall, biogas offers significant advantages in terms of renewable energy, waste management, environmental sustainability, and economic benefits. Its versatile applications make it a promising solution for meeting energy needs while prioritizing sustainability.
What's Biomass Energy and How Can it Benefit You?
Biomass energy is a form of renewable energy that utilizes organic materials to generate heat, electricity, and fuel. Let's address some common questions about biomass energy and its benefits:
1. What is biomass energy?
Biomass energy is derived from organic materials such as wood, crop residues, agricultural waste, and dedicated energy crops. These materials can be burned directly or converted into biofuels to generate heat, electricity, and transportation fuels.

2. How is biomass energy produced?
Biomass energy can be produced through processes such as:
- Combustion: Organic materials are burned directly to produce heat or electricity.
- Gasification: Biomass is converted into a gas by heating it in a low-oxygen environment.
- Anaerobic digestion: Organic waste is broken down by bacteria in the absence of oxygen, producing biogas.
- Biochemical conversion: Enzymes or microorganisms break down biomass into sugars, which can then be used to produce biofuels.
3. What are the advantages of biomass energy?
Biomass energy offers several advantages, including:
- Renewable and abundant: Biomass resources are renewable and readily available, reducing reliance on finite fossil fuels.
- Carbon neutral: The combustion or conversion of biomass does not introduce additional carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, as the carbon released is part of the natural carbon cycle.
- Waste management solution: Biomass energy can utilize agricultural waste, forest residues, and other organic materials that would otherwise contribute to waste management challenges.
- Local economic development: Biomass energy projects can create jobs, support local economies, and promote sustainable land use practices.
4. Can biomass energy help reduce greenhouse gas emissions?
Yes, biomass energy can contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. When organic materials are used for energy production, the carbon released during combustion or conversion is offset by the carbon absorbed by plants during photosynthesis. This makes biomass energy a carbon-neutral or even carbon-negative option, depending on the source and management practices.
5. How can biomass energy benefit households?
Biomass energy can benefit households in several ways:
- Heating and cooking: Biomass stoves and boilers can provide affordable and sustainable heating and cooking options, particularly in rural areas.
- Cost savings: Using biomass for heat or electricity can help reduce energy costs, especially when compared to fossil fuel alternatives.
- Energy independence: Producing biomass energy locally reduces dependence on imported fuels and promotes self-sufficiency.
6. What are the challenges of biomass energy?
While biomass energy has numerous benefits, there are also challenges that need to be addressed:
- Sustainability: Biomass resources need to be managed sustainably to avoid negative environmental impacts, such as deforestation or overharvesting.
- Efficiency: Maximizing energy conversion efficiency is crucial to make biomass energy a viable and competitive option.
- Air pollution: Inefficient combustion or improper biomass handling can result in air pollutants, such as particulate matter or volatile organic compounds.
7. Can biomass energy be used for transportation?
Yes, biomass energy can be converted into biofuels, such as ethanol and biodiesel, which can be used as alternative fuels for transportation. Biofuels derived from biomass can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels, lower carbon emissions, and promote sustainable transportation.
8. Is biomass energy suitable for large-scale power generation?
Biomass energy can be used for large-scale power generation, especially in areas with a consistent supply of biomass feedstock. Biomass power plants utilize steam turbines or gasification technologies to generate electricity. However, the availability and sustainability of biomass resources need to be carefully evaluated when considering large-scale implementation.
9. Can biomass energy support rural development?
Yes, biomass energy projects have the potential to support rural development in multiple ways:
- Job creation: Biomass energy projects require labor for feedstock collection, processing, and operation, creating employment opportunities in rural areas.
- Localized energy production: Biomass plants can provide decentralized energy solutions, reducing the need for extensive grid infrastructure in remote areas.
- Agricultural diversification: Growing dedicated energy crops for biomass production can diversify agricultural activities and provide additional income streams for farmers.
10. Can individuals contribute to biomass energy production?
Individuals can contribute to biomass energy production by:
- Using biomass stoves or boilers for heating and cooking.
- Participating in local biomass energy projects, such as community-based initiatives or cooperatives.
- Supporting sustainable forestry practices and promoting responsible biomass sourcing.
In conclusion, biomass energy offers a sustainable and versatile solution for heat, electricity, and fuel generation. It has numerous benefits, including its renewable nature, waste management potential, and potential for local economic development. However, careful consideration of sustainability and efficiency is crucial for maximizing the benefits of biomass energy.
Post a Comment for "how can biomass be used as an energy source"