how can biomass energy be negative to the environment
Negative Environmental Impacts of Renewable Energy
1. What are the negative environmental impacts of renewable energy?
Renewable energy sources have many positive environmental benefits, but they also have some negative impacts. Some of the negative environmental impacts of renewable energy include:
- Land and habitat disruption: The development of renewable energy projects, such as wind farms or solar power plants, can require a large amount of land. This can lead to habitat fragmentation and disruption for wildlife populations.
- Visual impact: Certain forms of renewable energy infrastructure, like wind turbines or solar panels, can have a visual impact on the landscape, which some people may find aesthetically unappealing.
- Water use: Certain types of renewable energy projects, such as hydropower dams or bioenergy plants, can require significant amounts of water for operation. This can impact local water supplies and aquatic ecosystems.
- Noise pollution: Some types of renewable energy infrastructure, such as wind turbines or tidal energy devices, can generate noise during operation, which can affect nearby communities or wildlife.
It is important to carefully consider and mitigate these negative impacts while harnessing the benefits of renewable energy sources.
2. How does the development of renewable energy projects affect wildlife?
The development of renewable energy projects, such as wind farms or solar power plants, can have both positive and negative impacts on wildlife:
- Habitat disruption: The construction of renewable energy infrastructure can lead to the disruption and fragmentation of wildlife habitats. This can result in the displacement or loss of certain wildlife populations.
- Collision risk: Wind turbines, in particular, can pose a collision risk for birds and bats. The spinning blades can be hazardous for flying animals, especially during migration seasons.
- Noise disturbance: Some types of renewable energy infrastructure, such as wind turbines or tidal energy devices, can generate noise during operation. This noise can disturb wildlife and affect their behavior and communication patterns.
- Positive impacts: On the other hand, certain renewable energy projects, like offshore wind farms, can provide habitats for marine species. These structures can serve as artificial reefs and attract marine life.
Environmental impact assessments and careful site selection can help minimize the negative impacts on wildlife and promote biodiversity conservation.

3. What are the potential effects of renewable energy on water resources?
Renewable energy projects can have various effects on water resources:
- Hydropower: Hydropower projects, such as dams, can have significant impacts on water resources. They can alter natural river flows, affect aquatic ecosystems, and disrupt fish migration patterns.
- Bioenergy: Biomass energy production can require significant amounts of water for processes like irrigation or cooling. This can place pressure on local water supplies, especially in regions already facing water scarcity.
- Solar and wind: Solar and wind energy technologies generally have minimal direct impacts on water resources. However, water may be indirectly used in the manufacturing and maintenance processes of these technologies.
It is crucial to consider the water requirements of renewable energy projects and implement sustainable water management practices to minimize any negative impacts on water resources.
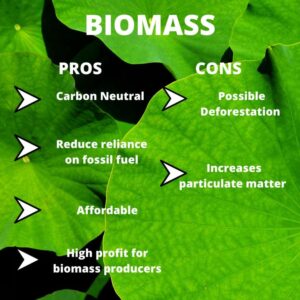
4. How does biomass energy benefit the environment?
Biomass energy can offer several environmental benefits:
- Renewable and carbon-neutral: Biomass is derived from organic sources such as agricultural residues, forestry wastes, or dedicated energy crops. As these sources are renewable, biomass energy is considered a sustainable energy option. When properly managed, it can be carbon-neutral, meaning it does not contribute additional greenhouse gas emissions to the atmosphere.
- Waste reduction: Utilizing biomass for energy production can help reduce the amount of organic waste sent to landfills. This can contribute to reducing methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas, from decomposing organic matter.
- Local economic benefits: Biomass energy projects can create jobs and support local economies, particularly in rural areas where biomass resources are abundant.
- Support for forestry and agriculture: The cultivation and harvesting of dedicated energy crops for biomass energy production can provide additional income opportunities for farmers and promote sustainable land management practices.
However, it is important to ensure that biomass resources are harvested sustainably and that the overall lifecycle impact of biomass energy, including transportation and processing, is carefully evaluated.

5. Are there any health concerns associated with renewable energy?
While renewable energy sources contribute to cleaner air and reduced pollution compared to fossil fuels, there can still be some health concerns:
- Noise pollution: Certain renewable energy technologies, such as wind turbines or tidal energy devices, can generate noise during operation. Prolonged exposure to high levels of noise can have negative impacts on human health, including sleep disturbance and stress.
- Electromagnetic fields: Some people have expressed concerns about potential health effects associated with exposure to the electromagnetic fields generated by certain renewable energy infrastructure, like power lines or solar panel installations. However, scientific studies have generally not found conclusive evidence linking these fields to adverse health effects.
- Occupational hazards: Workers involved in the installation, operation, and maintenance of renewable energy projects may face specific occupational hazards, such as falls from heights or exposure to chemicals during manufacturing processes. Appropriate safety measures and regulations are necessary to minimize these risks.
Overall, the health concerns associated with renewable energy are generally outweighed by the significant health benefits derived from reducing pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.

6. How does renewable energy contribute to mitigating climate change?
Renewable energy plays a vital role in mitigating climate change:
- Reduced greenhouse gas emissions: Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydro, and biomass, produce little to no direct greenhouse gas emissions during operation. By replacing fossil fuel-based energy generation, renewable energy significantly reduces the overall emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases, which are major contributors to climate change.
- Enhanced energy efficiency: The production of renewable energy technologies has become more energy-efficient over time. This means that less energy is required to manufacture and install renewable energy systems, resulting in a reduced carbon footprint.
- Transition to a low-carbon economy: The growth of renewable energy industries creates opportunities for economic development and the transition to a low-carbon economy. This transition involves moving away from fossil fuels, reducing dependence on imports, and promoting domestic clean energy production.
By accelerating the adoption of renewable energy, countries can make significant progress in addressing climate change and achieving their greenhouse gas reduction targets set under international agreements.

7. Can renewable energy alone meet all our energy needs?
While renewable energy is an important part of the energy mix, it is unlikely to meet all our energy needs alone, at least in the near future:
- Intermittency: Renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind, are intermittent, meaning they depend on weather conditions and are not always available in consistent quantities. Energy storage technologies, such as batteries, can help mitigate this issue but are still evolving and not yet capable of providing large-scale, long-duration storage.
- Geographic limitations: Some renewable energy sources are location-specific. For example, solar energy generation is most effective in regions with abundant sunlight, and hydropower relies on suitable water resources. Not all areas have the same renewable energy potential, which can limit the widespread deployment of certain technologies.
- Energy demand: With the increasing global energy demand, it may be challenging for renewable energy sources alone to meet the growing needs. Energy efficiency measures and demand-side management strategies are crucial in reducing overall energy consumption and optimizing the use of renewable energy.
A diversified energy mix that combines renewable energy with other sources, such as nuclear power or fossil fuels with carbon capture and storage, is often considered a more realistic approach to meeting energy needs while transitioning to a sustainable future.

8. What are the economic benefits of investing in renewable energy?
Investing in renewable energy can bring several economic benefits:
- Job creation: Renewable energy industries have the potential to create a significant number of jobs, both in manufacturing and installation as well as operations and maintenance. This can contribute to local economic development and employment opportunities.
- Energy cost stability: Renewable energy sources offer the advantage of long-term price stability. Unlike fossil fuels, which can be subject to price volatility due to geopolitical factors, renewables rely on free and abundant resources like sunlight and wind.
- Reduced reliance on fossil fuel imports: Countries heavily reliant on imported fossil fuels can enhance their energy security by investing in domestic renewable energy production. This reduces dependence on external suppliers and creates a more self-sufficient energy system.
- Technological innovation and competitiveness: The growth of renewable energy industries drives technological advancements and fosters innovation. This can lead to the development of new knowledge, expertise, and export opportunities, enhancing a country's competitiveness in the global market.
Additionally, prioritizing renewable energy can help reduce healthcare costs associated with air pollution and climate change impacts, creating further economic benefits for society as a whole.

9. How can the negative impacts of renewable energy be mitigated?
To mitigate the negative impacts of renewable energy, several strategies can be implemented:
- Site selection: Careful consideration of the location and site for renewable energy projects can help minimize impacts on sensitive habitats, wildlife populations, and local communities. Conducting thorough environmental impact assessments and involving stakeholders in the decision-making process are key components.
- Design and technology improvements: Continual advancements in renewable energy technologies can help reduce their negative impacts. For example, exploring innovative designs for wind turbines to minimize bird and bat collisions or implementing noise reduction measures for wind farms.
- Conservation and biodiversity planning: Enhancing conservation efforts and implementing biodiversity-friendly practices can help offset the habitat disruption caused by renewable energy projects. This can include habitat restoration, creation of wildlife corridors, and land set-asides for conservation purposes.
- Incorporating ecosystem services: Renewable energy projects can be designed to provide additional ecosystem services, such as enhancing pollinator habitats or improving water quality. This approach promotes a more holistic and sustainable approach to energy development.
By integrating these mitigation strategies into project planning and implementation, the negative impacts of renewable energy can be effectively reduced, allowing for a more balanced and sustainable energy transition.

10. What role does government policy play in promoting renewable energy?
Government policies and regulations have a significant impact on the promotion and development of renewable energy:
- Financial incentives: Governments can provide financial incentives, such as tax credits or feed-in tariffs, to support the deployment of renewable energy technologies. These incentives can make renewable energy more economically viable and attractive to investors.
- Renewable portfolio standards: Governments can establish targets or mandates for the share of renewable energy in the overall energy mix. Renewable portfolio standards require utilities or energy suppliers to procure a certain percentage of their energy from renewable sources, creating a market demand for renewable energy.
- Research and development funding: Governments can allocate funds for research and development in renewable energy technologies. This helps drive innovation, improve the efficiency of existing technologies, and develop new solutions to overcome challenges.
- Regulatory frameworks: Governments can establish regulations and standards to ensure the safe and sustainable deployment of renewable energy projects. These frameworks provide guidance on aspects such as environmental impact assessments, grid integration, and grid reliability.
Government policies play a crucial role in creating an enabling environment for renewable energy investment, fostering market competition, and accelerating the transition to a cleaner energy future.

11. What are the challenges in scaling up renewable energy deployment?
Scaling up renewable energy deployment presents several challenges:
- Intermittency and storage: Integrating large amounts of intermittent renewable energy into the grid requires effective energy storage solutions. Developing cost-effective and scalable energy storage technologies that can accommodate the variable nature of renewables is essential.
- Grid integration and infrastructure: Expanding renewable energy capacity often requires significant upgrades to the electricity grid infrastructure. This includes transmission lines, substations, and smart grid technologies to accommodate the distribution and management of renewable energy.
- Land and resource availability: The availability of suitable land and resources, such as wind or sunlight, can limit the potential for scaling up certain types of renewable energy projects. Managing competing land uses and addressing land tenure issues are important considerations.
- Technological advancements and costs: While renewable energy costs have significantly decreased in recent years, further technological advancements and cost reductions are necessary to achieve widespread affordability and competitiveness with conventional energy sources.
Addressing these challenges requires collaboration between governments, industry stakeholders, and researchers to develop innovative solutions and create supportive policies and frameworks.

12. How can individuals contribute to the adoption of renewable energy?
Individuals can play a significant role in driving the adoption of renewable energy:
- Installing rooftop solar panels: Homeowners can invest in installing solar panels on their rooftops to generate clean and renewable electricity for their own use. This not only reduces dependence on the grid but also contributes to the overall increase in renewable energy capacity.
- Choosing renewable energy providers: Individuals can support renewable energy by choosing electricity providers that offer renewable energy options. Many utility companies now offer green energy programs, allowing customers to obtain a portion or all of their electricity from renewable sources.
- Conserving energy: Conserving energy and increasing energy efficiency at the individual level can reduce overall energy demand and the need for additional energy generation. Simple actions like turning off lights when not in use, using energy-efficient appliances, and properly insulating homes can make a difference.
- Sustainable transportation choices: Opting for greener transportation options, such as using public transportation, carpooling, biking, or driving electric vehicles, can help reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
Collectively, individual actions can create a significant impact and drive the demand for renewable energy, leading to a more sustainable and cleaner energy future.

Conclusion
Renewable energy sources offer many benefits, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, and enhanced energy security. However, it is essential to acknowledge
Post a Comment for "how can biomass energy be negative to the environment"